Architecture
Central aspects of the linkki Frameworks are
-
the declarative definition of UIs via annotations
-
the flexible data binding
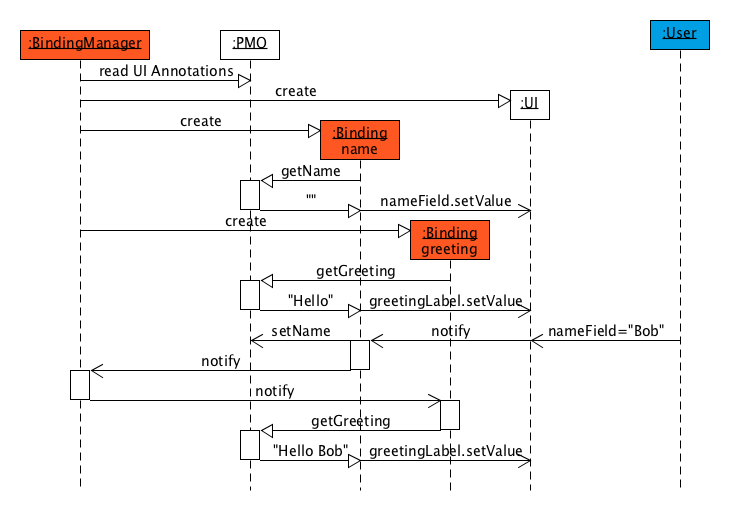
linkki enables a declarative definition of UIs, by generating them automatically from annotations. Additionally, content (data) of an UI element and its properties (for instance visibility, editability, …) can be bound to so called Presentation Model Objects (PMOs). With this, a bi-directional update mechanism is provided, the so called data binding. If a value is changed on the UI by a user, for instance, the corresponding value in the domain model is updated, as well as dependent properties and other UI elements.

In the first part of this chapter the BindingContext and BindingManager basics, and how they interact, are detailed.
Further on, Data binding with PMOs is explained. These can be simple PMOs, in which values are stored, or PMOs with domain model binding, where values are bound directly to the domain model. The binding of multiple model objects in a PMO is also explained.
Which properties of the defined UI elements can be controlled and which possibilities linkki provides, is discussed in the section Binding of further UI element properties.
The chapter concludes with Cross-Sectional Data Binding.
BindingContext Basics
Data Binding with PMOs
Data on Multiple Layers
Binding further UI properties
Cross-Sectional Data Binding
